 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|||||||
| Signals | Systems | System Response | |||||
| Frequency Representation | Fourier Series / Transforms | Background Material | |||||
Dirac Delta
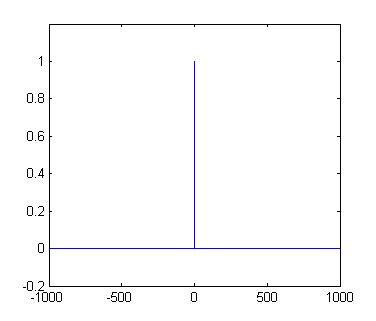
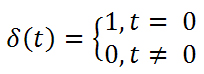
Properties or theorems involving Dirac delta function
- Sampling theorem
Continuous
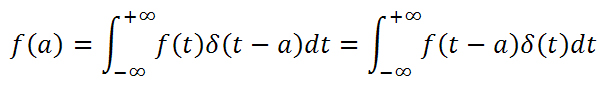
Discrete
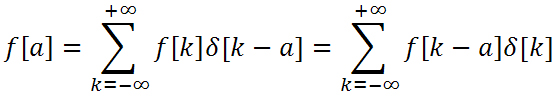
How is this used?
Ex. Solve the integral.
![]()
![]()
- Integral of Dirac delta function
![]()
Unit Step function
The unit step function is a unique function that is zero up until t = 0, then becomes one until +∞.
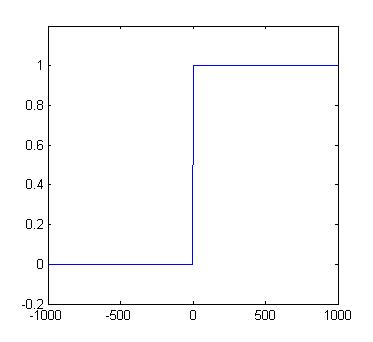
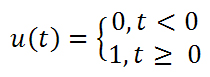
Derivative of Unit Step Function
![]()
Complex Exponential
Let us define Euler's formula as:
![]()
We can then define a transformation from polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates as:
![]()
![]()
The reverse transformation can also be defined:
![]()
![]()
Most importantly, we need a way to define complex operations. Thus, let us define an x where
![]()
and a y where
![]()
Then, we can define addition and subtraction where the real terms add together and the imaginary terms add together.
![]()
![]()
For multiplication, it is most important to note that when two imaginary numbers multiply, the solution is real because ![]() . After multiplication, we also group the real terms with the real terms and the imaginary terms with the imaginary terms.
. After multiplication, we also group the real terms with the real terms and the imaginary terms with the imaginary terms.
![]()
For division, it is most important to remember to multiply the numerator and denominator by the complex conjugate of the denominator. This way we can make the denominator entirely real.
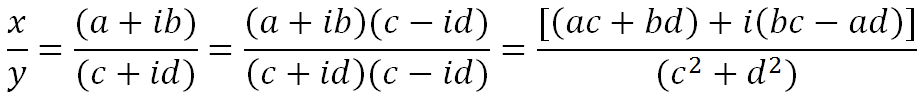
|
For comments and suggestions on this page, please click the link below: |